Coeliac Disease
What is Coeliac Disease?
Coeliac Disease (also called Celiac Disease) is an autoimmune condition where the body mistakenly attacks itself when gluten is consumed. Gluten is a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When someone with Coeliac Disease eats gluten, their immune system reacts by damaging the small intestine lining.
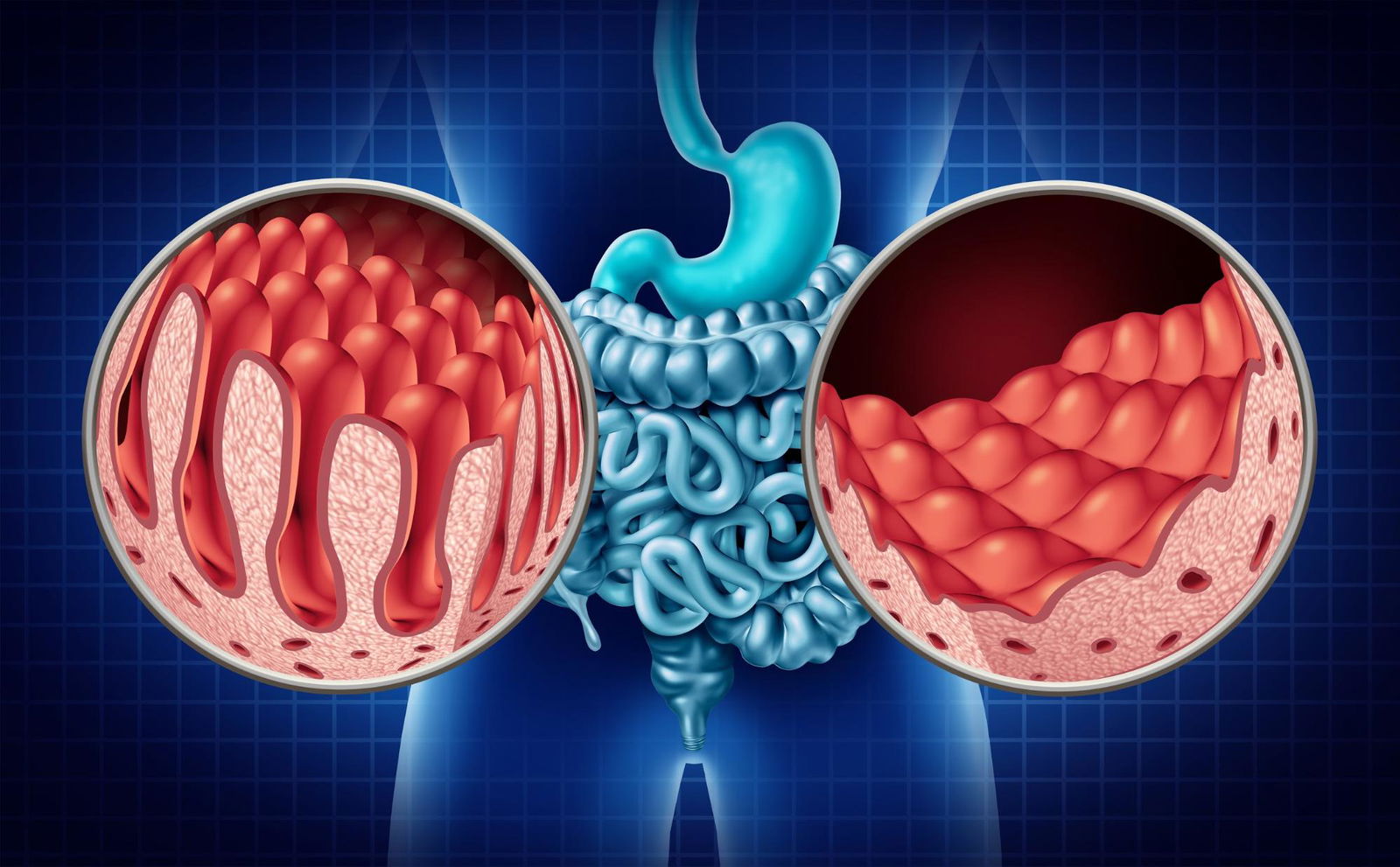
This damage affects the villi (tiny finger-like structures that absorb nutrients from food). This stops the body from absorbing the necessary nutrition it requires, causing stomach pain, diarrhoea, bloating, and exhaustion. If untreated, it can result in more serious health issues such as weakened bones, neurological problems, and even infertility.
The exact correlation of Coeliac Disease is not described in Ayurvedic classics, however symptoms similar to Coeliac Disease are discussed under the term ‘Grahani Dosha’. According to Ayurveda, Grahani Dosha arises from Agni-Dusti, which means the derangement of digestive fire. In Ayurveda, digestion is governed by Agni and assisted by the three Doshas. Any disturbance in Agni or Doshas can disturb digestion, resulting in diseases of the Annavaha Srotas (digestive system). This conceptual framework guides Ayurvedic practitioners in treating Coeliac Disease by restoring the digestive fire and correcting the Dosha imbalances to reduce the digestive symptoms of Coeliac Disease.
Understanding Coeliac Disease from a traditional Ayurvedic perspective might assist in controlling its symptoms and improving quality of life for patients. If you believe you might have Coeliac Disease, it is important to consult an Ayurvedic practitioner for prompt diagnosis and treatment.
Common Causes of Coeliac Disease
Coeliac Disease is primarily caused by both genetic and environmental factors, which make some individuals more vulnerable to this particular autoimmune condition. The exact cause is complex, but understanding common triggers may help manage and prevent Coeliac Disease symptoms from developing.
The most common causes of Coeliac Disease are:
Genetic Predisposition: The majority of people with Coeliac Disease carry specific genetic markers (HLA-DQ8 or HLA-DQ2). Having these genes doesn't mean the disease will develop automatically, but it increases the risk significantly.
Introduction of Gluten in Diet: The presence of gluten in the diet is necessary for Coeliac Disease to manifest. Gluten is found in wheat, barley, rye and their derivatives. The autoimmune response that damages the intestine is induced by gluten consumption.
Infant Feeding Practices: The timing of adding gluten to an infant's diet could impact the risk of developing Coeliac Disease, as per studies. Introducing gluten too soon or too late may increase this risk, although this relationship needs further study.
Gut Health: The overall health and state of the gut microbiome itself may also play a role. An imbalance in the gut bacteria or a history of gut infections could trigger Coeliac Disease by affecting the body's immune response.
Other Autoimmune Conditions: Various other autoimmune conditions like type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis or autoimmune thyroid disease, can place a person at greater risk of developing Coeliac Disease.
Environmental Stressors: There is some evidence that suggests that surgery, viral infections, pregnancy, childbirth, and excessive emotional stress may lead to Coeliac Disease in genetically predisposed individuals.
Signs and Symptoms of Coeliac Disease
Coeliac Disease affects everyone differently, causing mild to severe symptoms. Recognising the Coeliac Disease symptoms early may facilitate quicker diagnosis and management, reducing discomfort and preventing chronic health issues.
The most obvious signs & symptoms of Coeliac Disease in adults include:
Coeliac Symptoms
Digestive problems
Bloating, diarrhoea, gas, constipation and abdominal pain are some common symptoms which generally occur after having meals containing gluten.
Weight Loss & Fatigue
Many people experience unintended weight loss and chronic fatigue as the body fails to absorb nutrients properly.
Anaemia
Poor absorption of iron and other nutrients can lead to anaemia, as one of the initial symptoms of Coeliac Disease, causing exhaustion and pallor.
Skin Rash
A blistering skin disease, called dermatitis herpetiformis, is linked with Coeliac Disease. It usually appears on the elbows, knees and buttocks.
Mouth Problems
Recurring canker sores and a condition called “gluten cheilitis” (inflammation and redness around the mouth) are some other Coeliac Disease symptoms.
Neurological Symptoms
Some people also report headaches, poor concentration, or feeling "foggy-headed.
Bone & Joint Pain
Reduced calcium absorption could result in joint pain and osteoporosis.